SwiftUI 学习日志(9):列表和导航
欢迎来到《SwiftUI 学习日志》的第 9 篇文章。在本篇文章中,我们将深入探讨如何在 SwiftUI 中实现列表和导航。通过学习如何创建简单列表、自定义列表单元格,以及在列表中实现导航,您将能够构建出更加功能完善和用户友好的应用程序。
1. 列表
1.1 创建简单列表
在 SwiftUI 中,List 视图用于创建和显示列表,我们可以使用 List 来展示一组数据。List 视图的初始化方法之一是 List(_:id:content:),它接受一个标识符参数 id,用于唯一标识列表中的每个元素。
/// ### 1.1 创建简单列表
struct SimpleListView: View {
let items = ["苹果", "香蕉", "橙子", "西瓜"]
var body: some View {
List(items, id: \.self) { item in
Text(item)
}
}
}
#Preview {
SimpleListView()
}
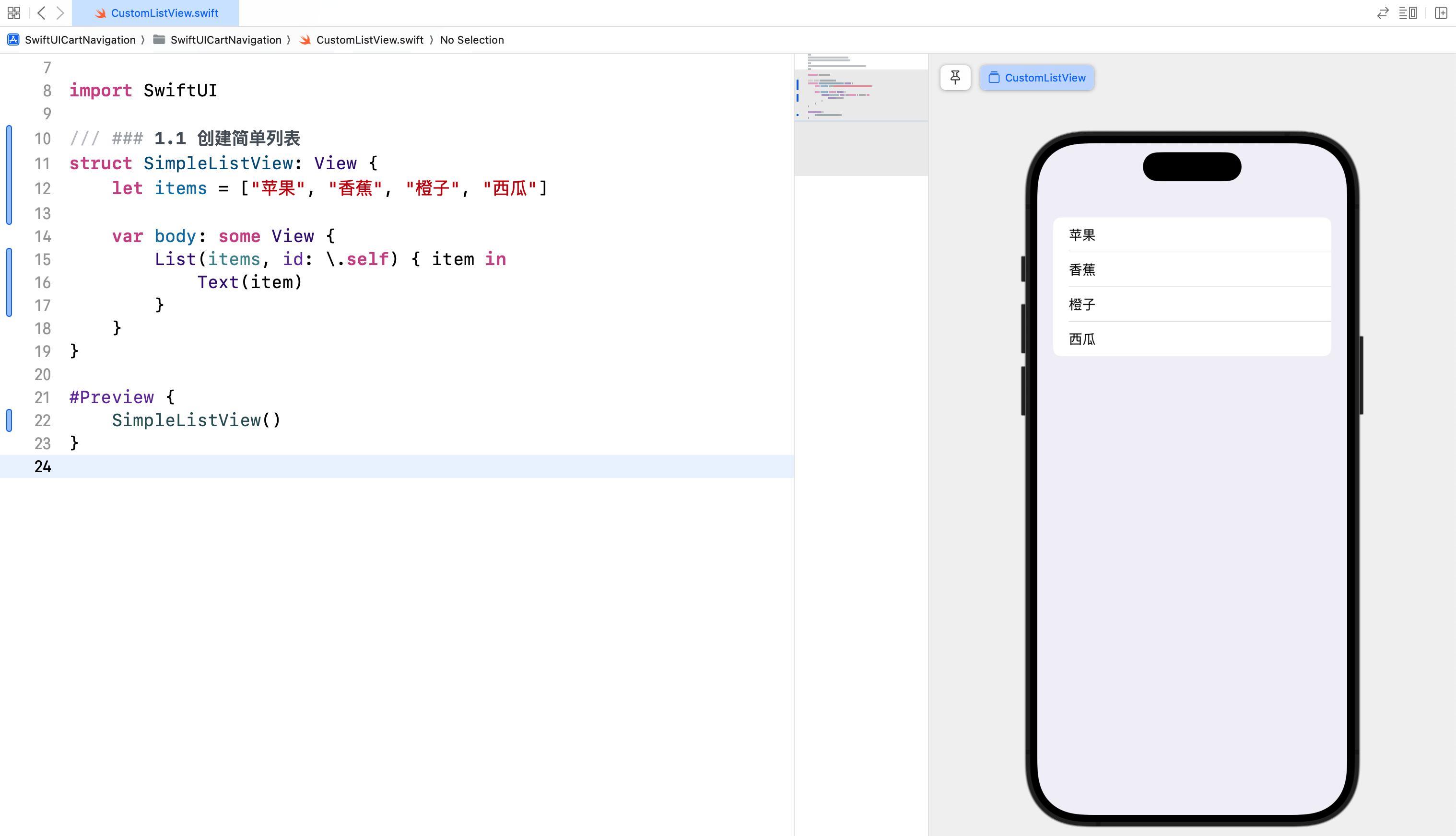
id: \.self 的作用
- 唯一标识符:在列表中,每个元素需要有一个唯一标识符,以便 SwiftUI 能够有效地识别和管理每个视图。当你提供
id: \.self时,SwiftUI 使用每个字符串值(例如"苹果"、"香蕉"等)作为唯一标识符。这是有效的,因为在这个列表中,每个字符串都是唯一的。 - 确保高效更新:如果列表中的数据发生变化,SwiftUI 可以通过这些唯一标识符有效地更新视图,而无需重新加载整个列表。
1.2 自定义列表单元格
在实际应用中,我们经常需要展示更复杂的列表项。通过自定义列表单元格,您可以将多种视图组合在一起,以显示更加丰富的信息。例如,可以添加图标、图片、标题、描述等。
/// ### 1.2 自定义列表单元格
struct CustomListView: View {
let items = ["苹果", "香蕉", "橙子", "西瓜"]
var body: some View {
List(items, id: \.self) { item in
HStack {
Image(systemName: "star.fill")
.foregroundColor(.yellow)
Text(item)
.font(.headline)
}
}
}
}
#Preview {
CustomListView()
}
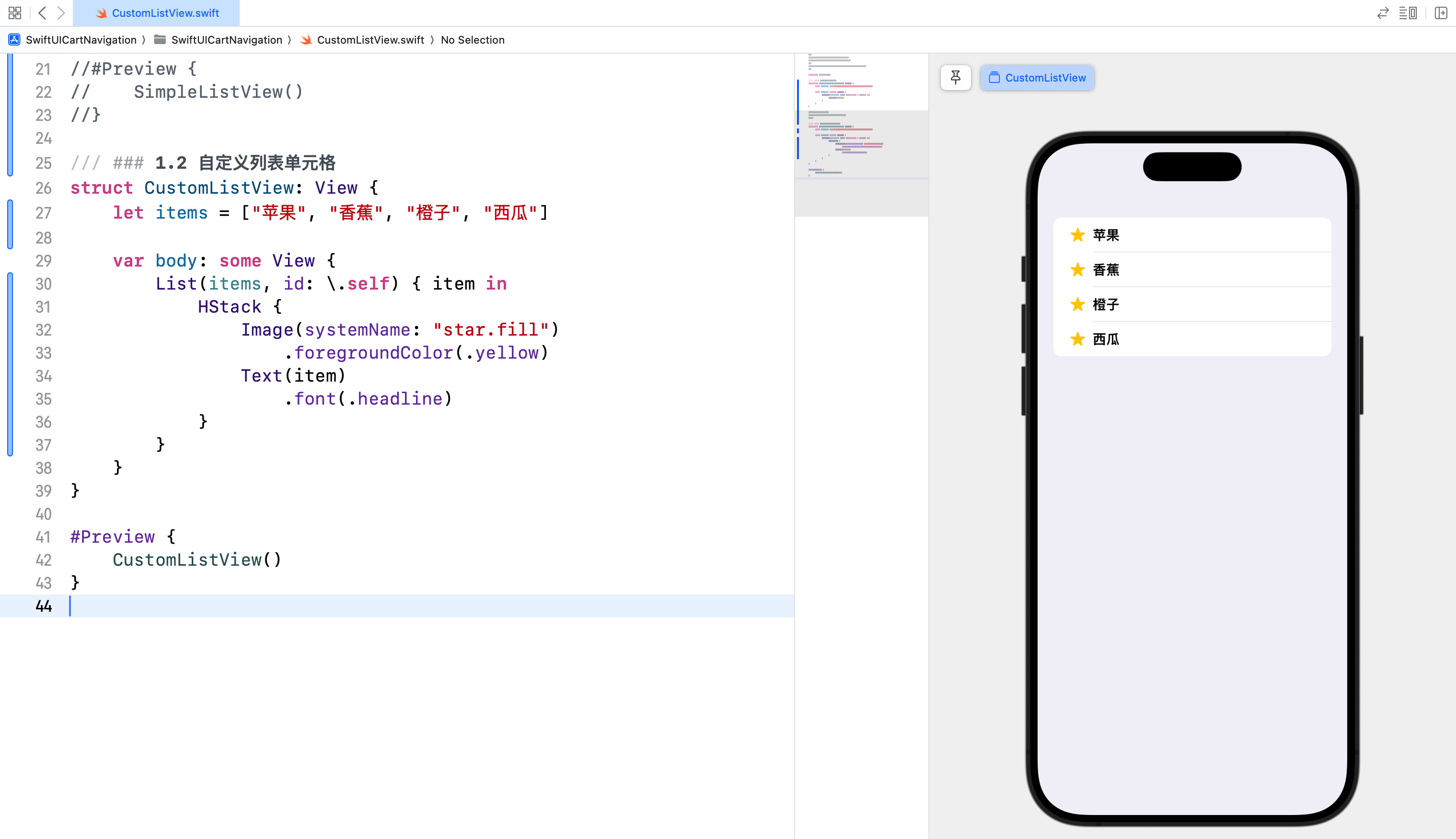
在这个示例中,我们使用 HStack 将一个图标和一个文本并排显示。Image(systemName:) 创建了一个系统图标,Text(item) 显示了列表项的文本内容。
1.3 动态列表
动态列表可以随着数据的变化而自动更新。在 SwiftUI 中,您可以使用 ForEach 和自定义的数据模型来创建动态列表。动态列表通常用于显示从网络请求或数据库中获取的数据。
/// ### 1.3 动态列表
struct Fruit: Identifiable {
/// ID 唯一标识符
var id = UUID()
/// 名称
var name: String
}
struct DynamicListView: View {
@State private var fruits = [
Fruit(name: "苹果"),
Fruit(name: "香蕉"),
Fruit(name: "橙子"),
Fruit(name: "西瓜")
]
@State private var newFruitName = ""
var body: some View {
VStack {
HStack {
TextField("输入水果名称", text: $newFruitName)
.textFieldStyle(RoundedBorderTextFieldStyle())
.padding()
Button("添加") {
addFruit()
}
.padding()
}
List(fruits) { fruit in
Text(fruit.name)
.font(.headline)
}
}
.padding()
}
/// 添加水果
private func addFruit() {
// 判断内容是否为空
guard !newFruitName.isEmpty else { return }
// 新建水果对象
let newFruit = Fruit(name: newFruitName)
// 添加到 fruits 数组
fruits.append(newFruit)
// 清空 newFruitName 达到清空文本框的效果
newFruitName = ""
}
}
#Preview {
DynamicListView()
}
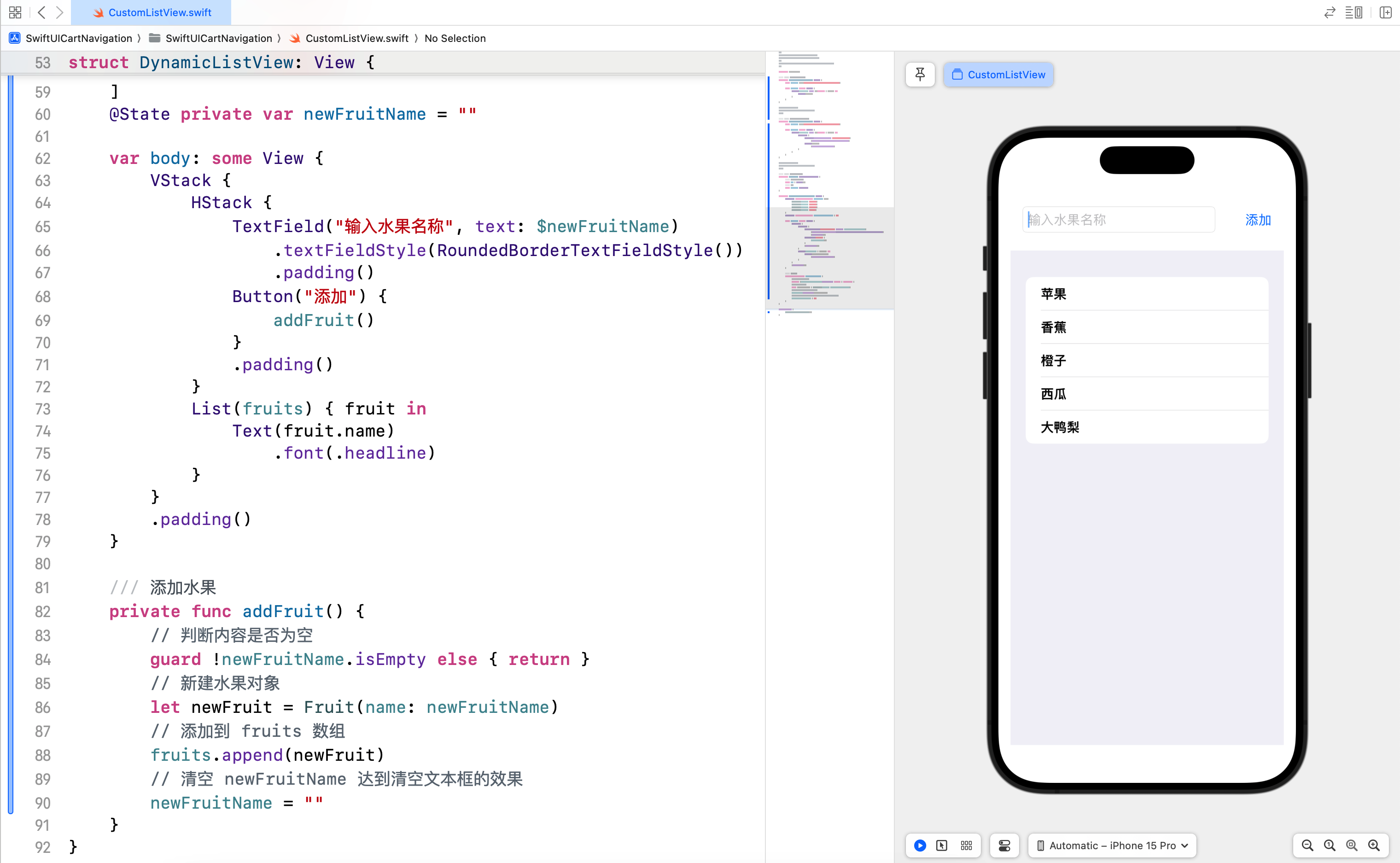
在这个示例中,我们定义了一个 Fruit 数据模型,它遵循 Identifiable 协议,这样 SwiftUI 可以识别每个水果项。然后,我们创建一个 List,使用 ForEach 遍历 fruits 数组,并为每个水果项创建一个 Text 视图。
同时我们在列表上方增加了一个输入框和添加按钮,用户输入的新的水果会被添加到 fruits 数组,同时随着数组内容的变化,列表显示可以自动更新。
1.4 Section 和 GroupedListStyle
Section 允许我们将列表分组,并使用 GroupedListStyle 设置列表的样式。这样可以更好地组织和显示数据。
/// ### 1.4 Section 和 GroupedListStyle
struct SectionedListView: View {
var body: some View {
List {
Section(header: Text("水果")) {
Text("苹果")
Text("香蕉")
}
Section(header: Text("蔬菜")) {
Text("西红柿")
Text("黄瓜")
}
}
.listStyle(GroupedListStyle())
}
}
#Preview {
SectionedListView()
}
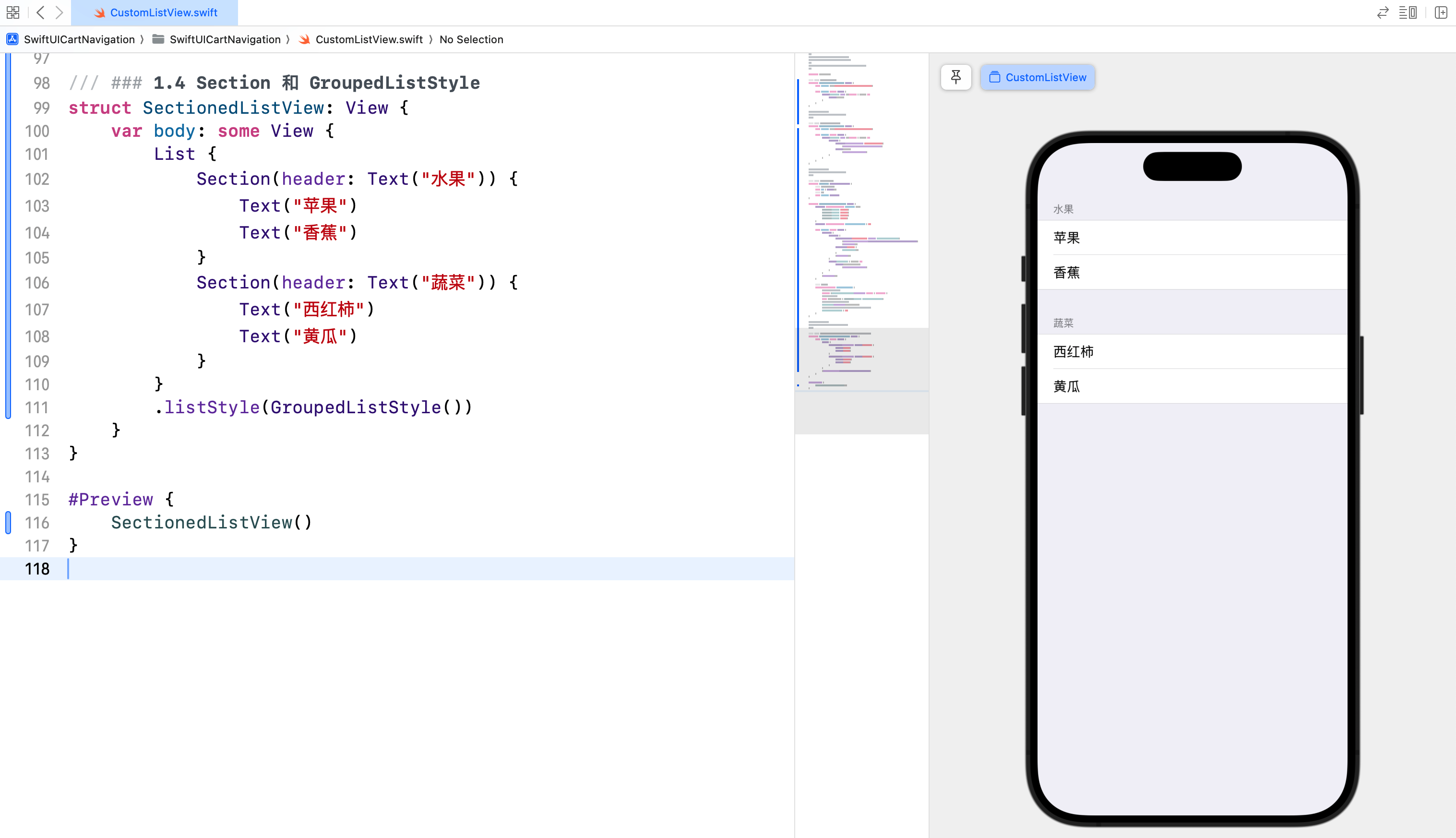
在这个示例中,我们使用 Section 将列表分成两部分:水果和蔬菜。每个 Section 有一个头部标题,并包含相关的列表项。GroupedListStyle 使列表看起来更加分组和有组织。
1.5 动态列表和静态列表
在一个列表中,我们可以同时使用动态和静态数据。通过这种方式,可以展示一些固定的和动态变化的数据。
/// ### 1.5 动态列表和静态列表
struct MixedListView: View {
let dynamicItems = ["苹果", "香蕉", "橙子"]
var body: some View {
List {
Section(header: Text("动态列表")) {
ForEach(dynamicItems, id: \.self) { item in
Text(item)
}
}
Section(header: Text("静态列表")) {
Text("西瓜")
Text("梨")
}
}
.listStyle(GroupedListStyle())
}
}
#Preview {
MixedListView()
}
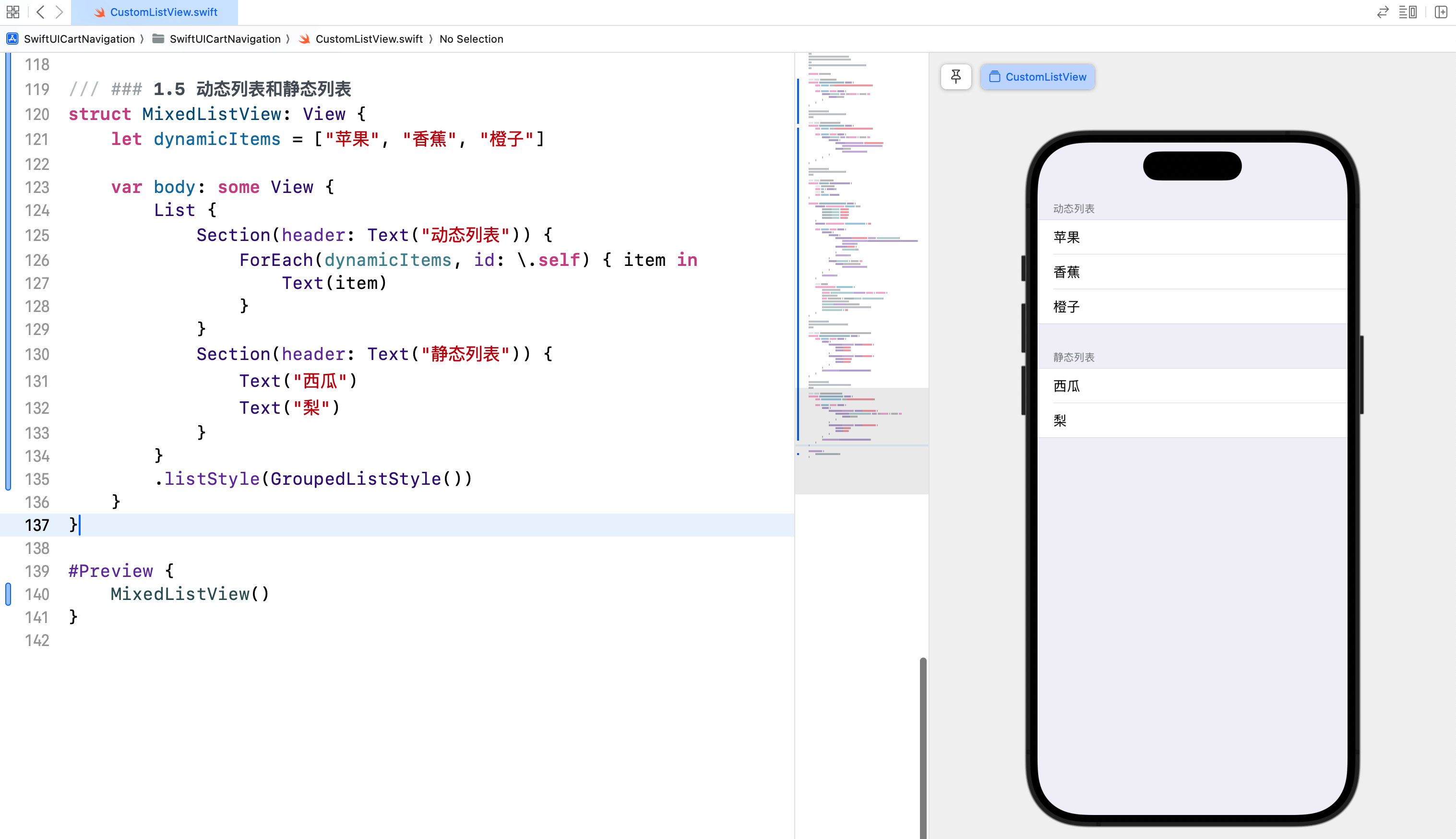
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个混合列表,其中一部分是动态数据(使用 ForEach),另一部分是静态数据(直接在列表中定义)。这种组合使用可以让我们在一个列表中展示多种类型的数据。
1.6 复杂单元格的定制
对于需要展示复杂信息的列表项,我们可以自定义列表单元格,以包含多种视图和布局。
/// ### 1.6 复杂单元格的定制
struct ComplexItemView: View {
var title: String
var subtitle: String
var images: [String]
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(title)
.font(.headline)
Text(subtitle)
.font(.subheadline)
.foregroundColor(.gray)
HStack {
ForEach(images, id: \.self) { image in
Image(systemName: image)
.resizable()
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
}
.padding()
}
}
struct ComplexListView: View {
let items = [
("新闻标题1", "发布时间:2024-01-01", ["photo", "globe", "heart", "house", "gear"]),
("新闻标题2", "发布时间:2024-01-02", ["cart", "bell", "camera", "book"]),
("新闻标题3", "发布时间:2024-01-03", [])
]
var body: some View {
List(items, id: \.0) { item in
ComplexItemView(title: item.0, subtitle: item.1, images: item.2)
}
}
}
#Preview {
ComplexListView()
}
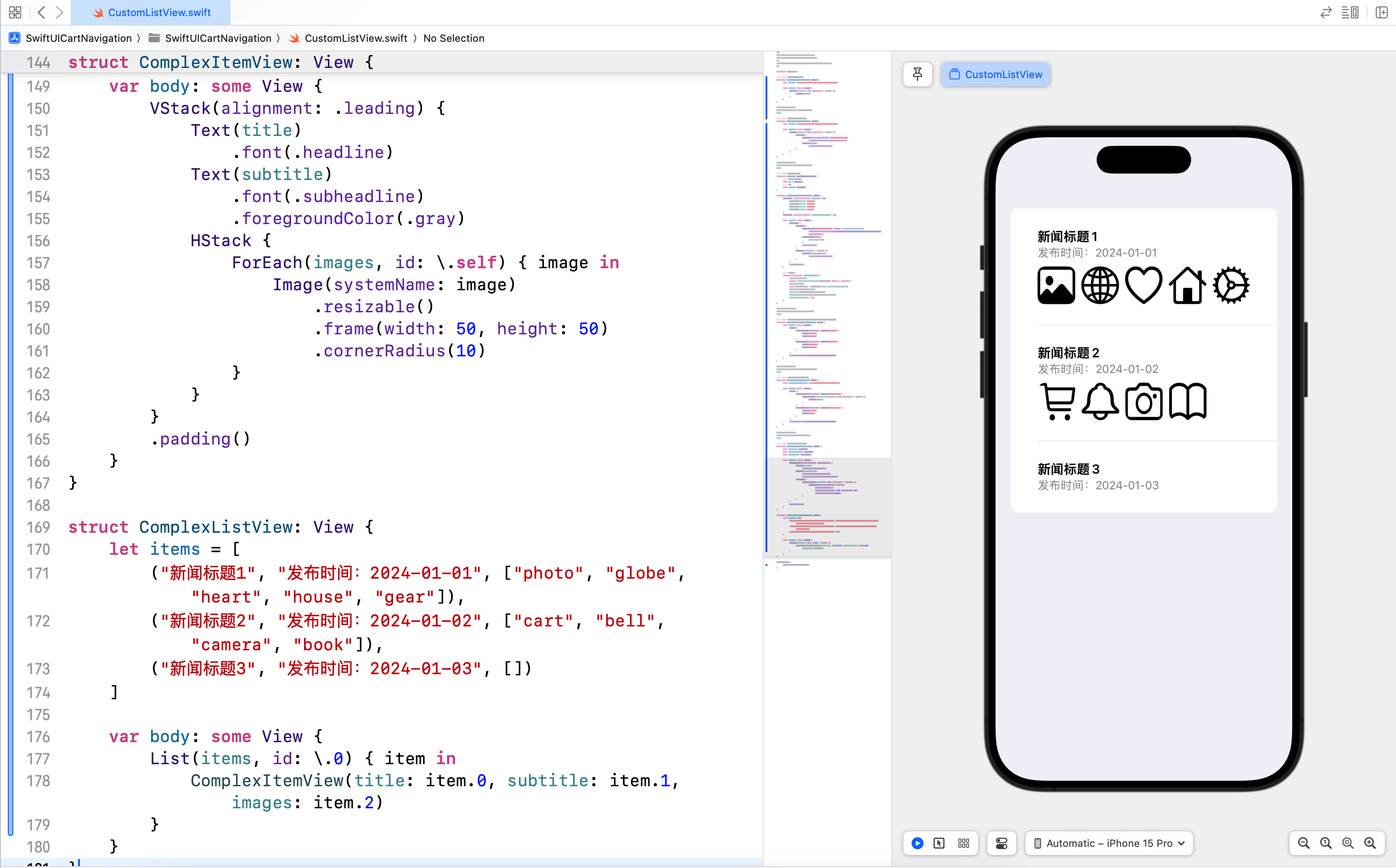
在这个示例中,ComplexItemView 显示了新闻的标题、发布时间和图片。通过 VStack 和 HStack,我们可以轻松地组织和排列这些视图。
2. 导航
2.1 使用 NavigationView 和 NavigationLink
NavigationView 是创建导航界面的基础,它可以容纳一个或多个 NavigationLink,用于在视图之间导航。NavigationLink 用于创建可导航的链接。
/// ### 2.1 使用 NavigationView 和 NavigationLink
struct NavigationExampleView: View {
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
VStack {
NavigationLink(destination: Text("这是第二个视图")) {
Text("点击导航到第二个视图")
.padding()
.background(.blue)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
.navigationTitle("导航示例")
}
}
}
#Preview {
NavigationExampleView()
}
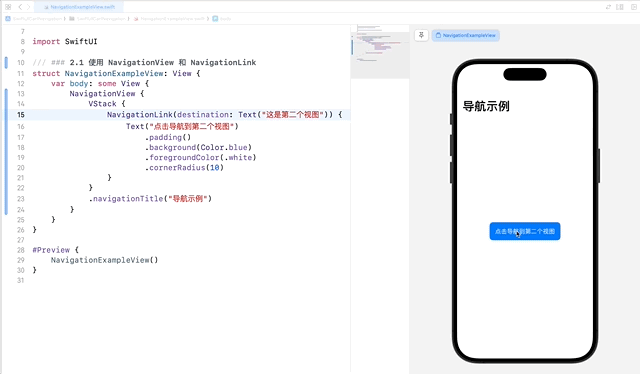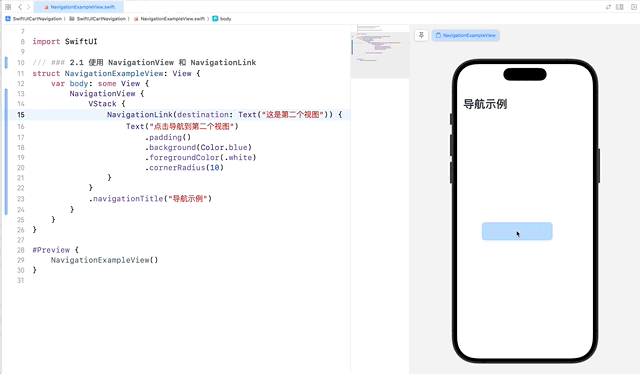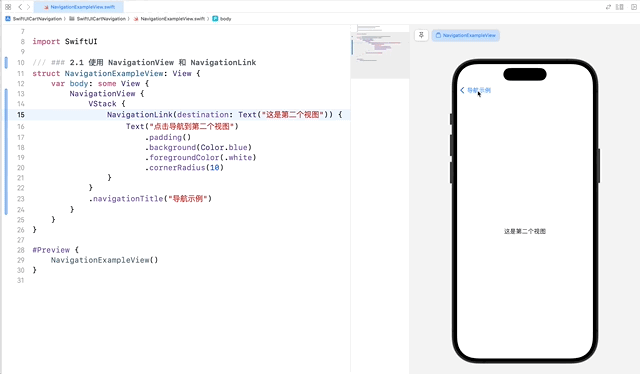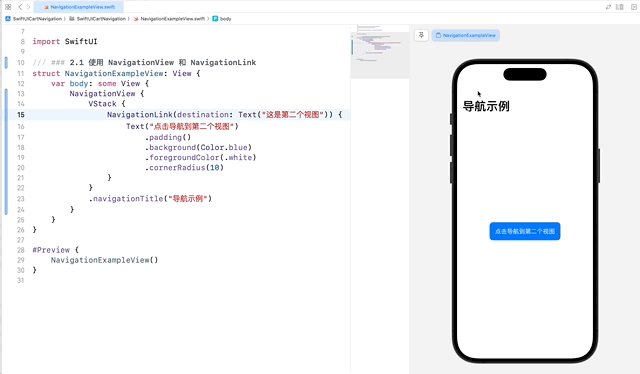
在这个示例中,NavigationLink 用于创建一个从当前视图到第二个视图的链接。当用户点击 Text 视图时,应用会导航到目标视图。
2.2 列表中的导航
在列表中使用 NavigationLink 可以实现从列表项到详细视图的导航。这使得我们可以点击列表中的项,进入到更详细的视图。
/// ### 2.2 列表中的导航
struct FruitDetailView: View {
var fruit: String
var body: some View {
Text("你选择了 \(fruit)")
.font(.largeTitle)
.padding()
}
}
struct NavigableListView: View {
let fruits = ["苹果", "香蕉", "橙子", "西瓜"]
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
List(fruits, id: \.self) { fruit in
NavigationLink(destination: FruitDetailView(fruit: fruit)) {
Text(fruit)
}
}
.navigationTitle("水果列表")
}
}
}
#Preview {
NavigableListView()
}
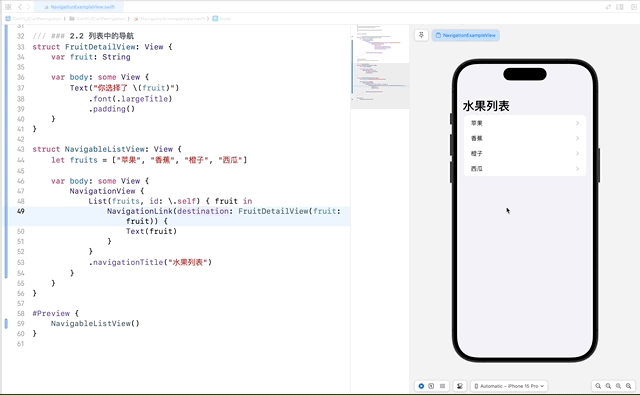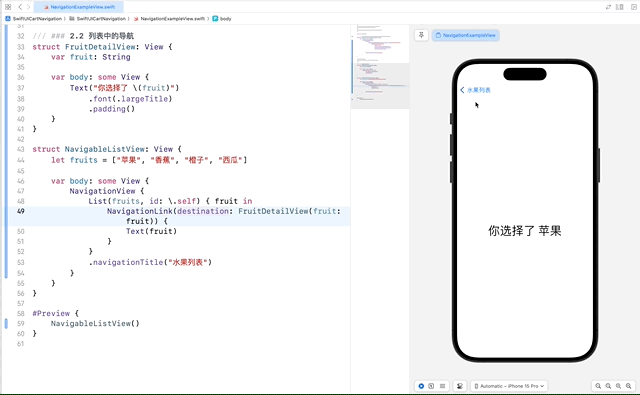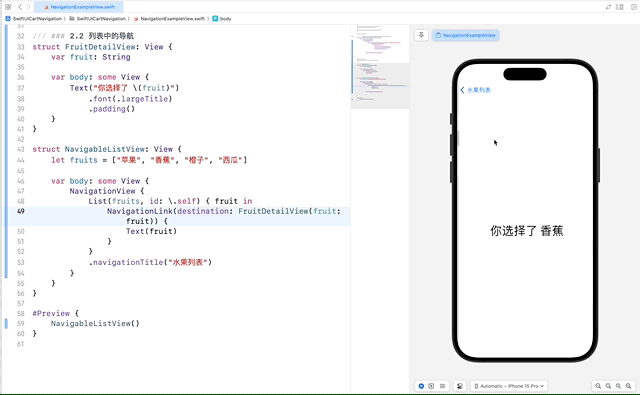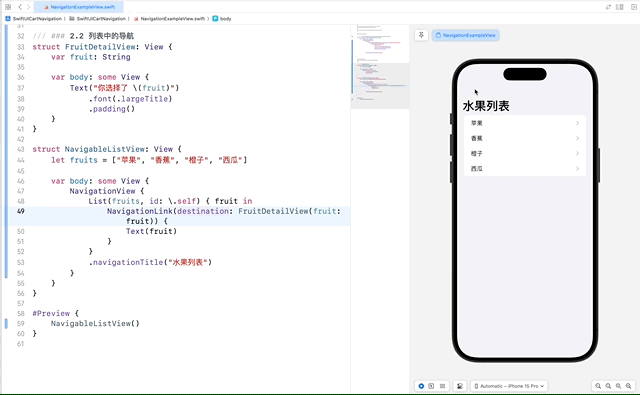
在这个示例中,每个列表项都包含一个 NavigationLink,它指向 FruitDetailView。当用户点击某个水果时,应用会导航到显示该水果详情的视图。
2.3 视图间的导航和传递数据
通过 NavigationLink 传递数据,实现视图间的导航和数据传递。这个功能非常适合在不同的视图之间传递复杂的数据模型。
/// ### 2.3 视图间的导航和传递数据
struct Item: Identifiable {
var id = UUID()
var name: String
var description: String
}
struct ItemDetailView: View {
var item: Item
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text(item.name)
.font(.largeTitle)
.padding()
Text(item.description)
.padding()
Spacer()
}
.navigationTitle("详细信息")
}
}
struct ItemListView: View {
let items = [
Item(name: "苹果", description: "一种美味的水果"),
Item(name: "香蕉", description: "富含钾的水果"),
Item(name: "橙子", description: "富含维生素C的水果")
]
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
List(items) { item in
NavigationLink(destination: ItemDetailView(item: item)) {
Text(item.name)
}
}
.navigationTitle("水果列表")
}
}
}
#Preview {
ItemListView()
}
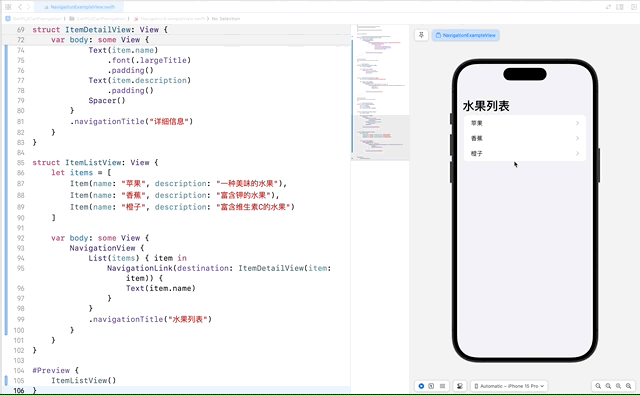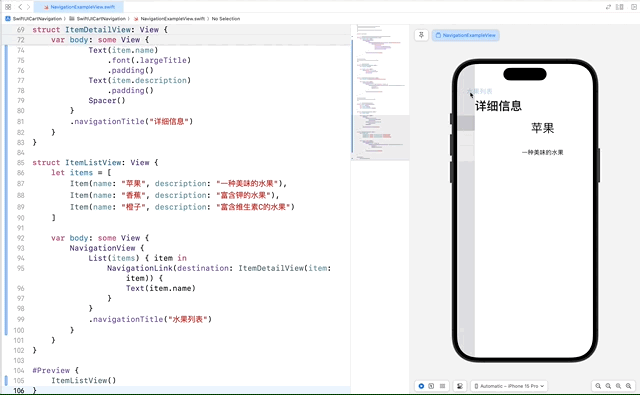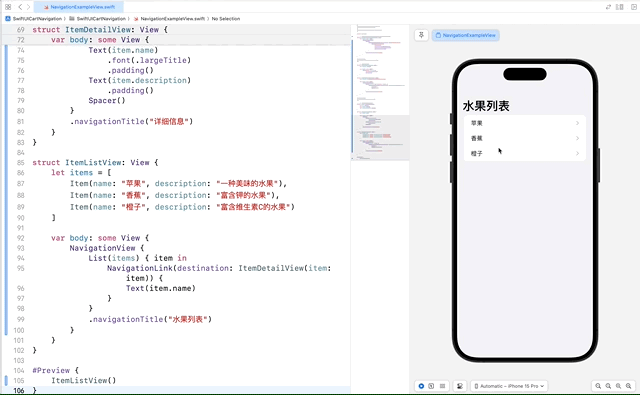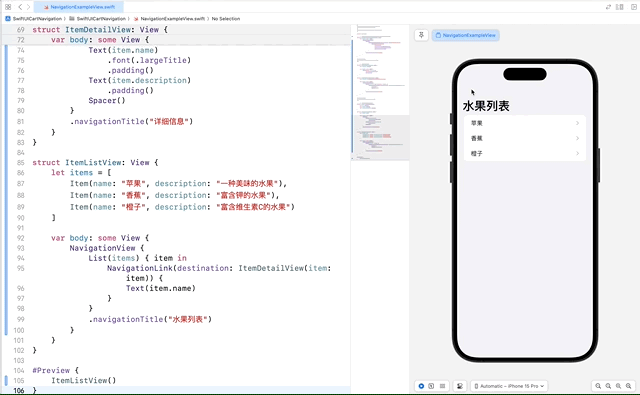
在这个示例中,我们定义了一个 Item 数据模型,并创建了 ItemDetailView 来显示每个项的详细信息。在 ItemListView 中,我们使用 NavigationLink 将每个列表项链接到对应的 ItemDetailView。
2.4 模态视图和全屏视图
通过 sheet 和 fullScreenCover 可以实现模态视图和全屏视图的展示效果。
/// ### 2.4 模态视图和全屏视图
struct ModalExampleView: View {
@State private var showModal = false
@State private var showFullScreen = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button("显示模态视图") {
showModal.toggle()
}
.padding()
.sheet(isPresented: $showModal) {
ModalContentView(isPresented: $showModal)
}
Button("显示全屏视图") {
showFullScreen.toggle()
}
.padding()
.fullScreenCover(isPresented: $showFullScreen) {
FullScreenContentView(isPresented: $showFullScreen)
}
}
}
}
struct ModalContentView: View {
@Binding var isPresented: Bool
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("这是一个模态视图")
.font(.largeTitle)
.padding()
Button("关闭") {
isPresented = false
}
.padding()
.background(.red)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
}
struct FullScreenContentView: View {
@Binding var isPresented: Bool
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("这是一个全屏视图")
.font(.largeTitle)
.padding()
Button("关闭") {
isPresented = false
}
.padding()
.background(.red)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
}
#Preview {
ModalExampleView()
}
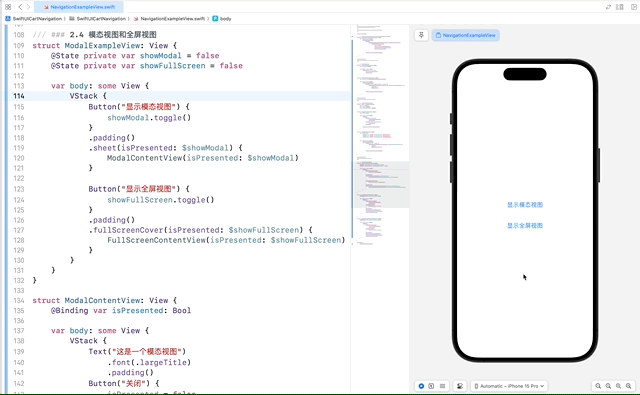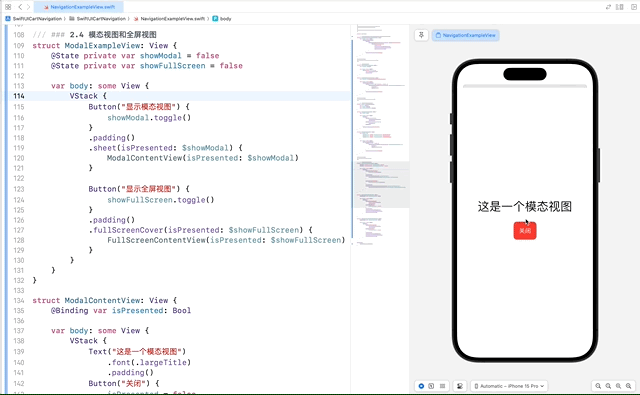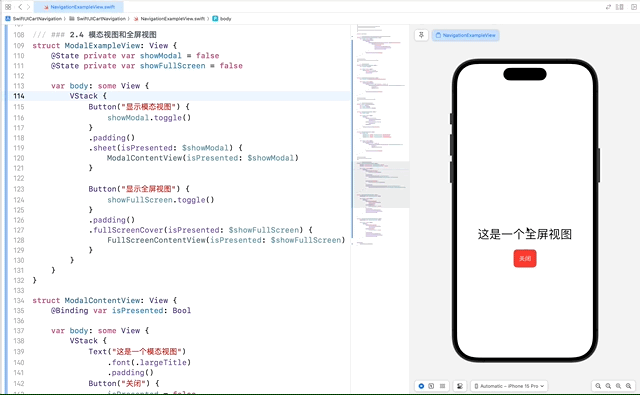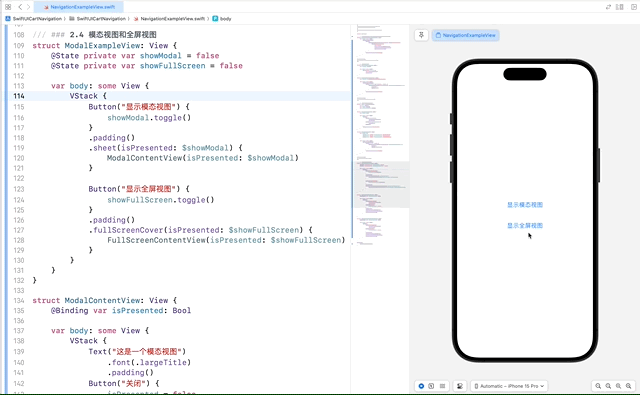
在这个示例中,ModalContentView 和 FullScreenContentView 都使用了一个 @Binding var isPresented: Bool 来接收绑定的状态,并在关闭按钮的点击事件中将其设置为 false,以关闭模态窗口或全屏视图。
3. 综合案例:购物车案例
3.1 案例简介
在这个综合案例中,我们将创建一个购物车应用,展示如何使用列表展示商品信息,并通过导航实现商品详情查看和购物车管理。我们将使用自定义单元格展示商品信息,并通过导航视图实现商品详情页面和购物车页面之间的导航。
3.2 商品数据模型
首先,我们定义商品数据模型 Product,包括商品名称、价格、描述和图像。
/// 商品数据模型
struct Product: Identifiable {
/// 唯一标识
var id = UUID()
/// 商品名称
var name: String
/// 价格
var price: Double
/// 商品描述
var description: String
/// 图像名称
var imageName: String
}
3.3 商品详情视图
商品详情视图 ProductDetailView 显示了商品的详细信息,并提供一个按钮将商品添加到购物车。
/// 商品详情视图
struct ProductDetailView: View {
var product: Product
@Binding var cart: [Product]
var body: some View {
VStack {
Image(systemName: product.imageName)
.resizable()
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.clipShape(Circle())
.padding()
Text(product.name)
.font(.largeTitle)
.padding()
Text("\(product.price, specifier: "%.2f") 元")
.font(.title)
.padding()
Text(product.description)
.padding()
Button("加入购物车") {
cart.append(product)
}
.padding()
.background(.blue)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
.navigationTitle(product.name)
}
}
#Preview {
ProductDetailView(product: Product(name: "商品1",
price: 10.0,
description: "这是商品1的描述",
imageName: "photo"),
cart: .constant([]))
}
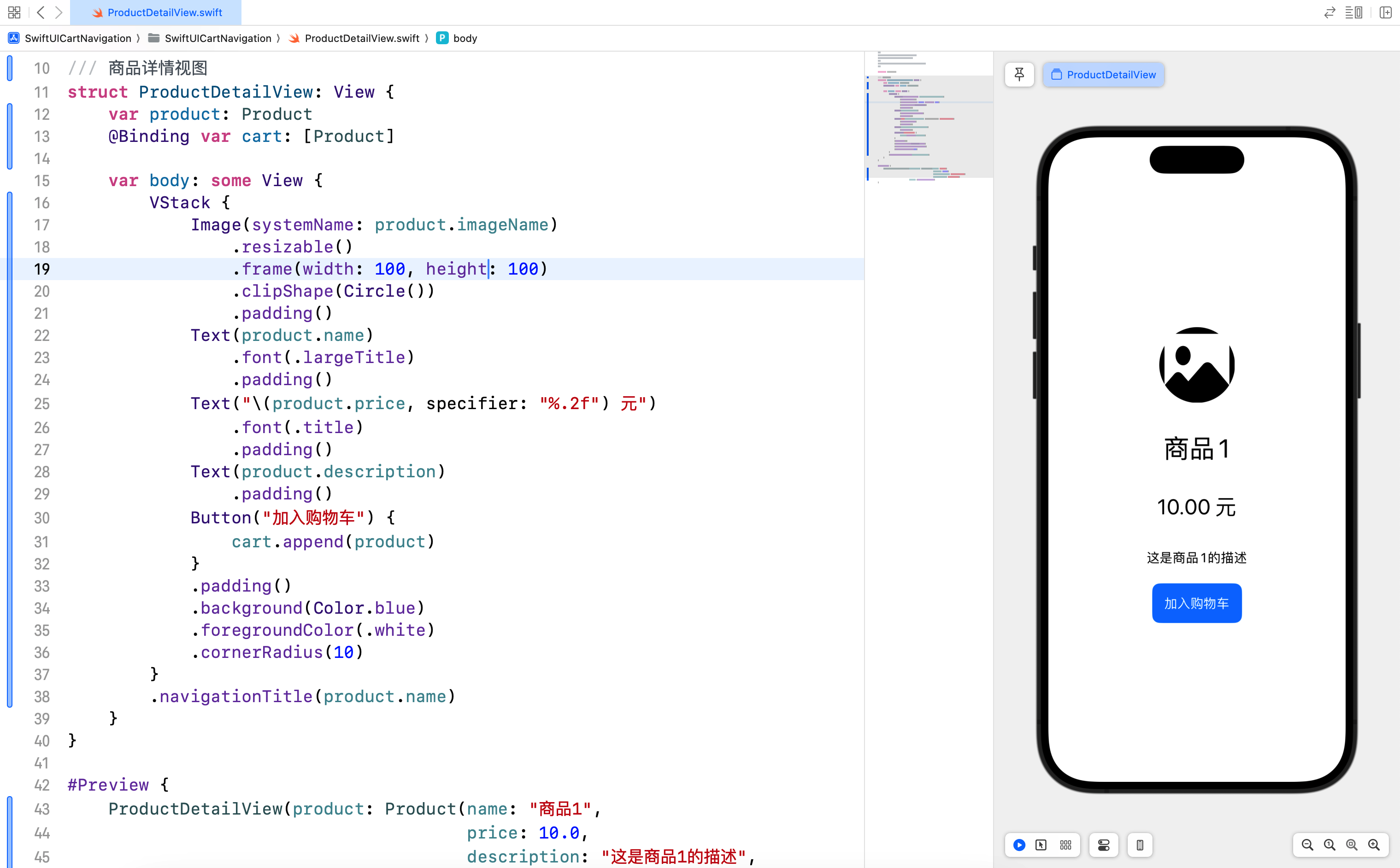
3.4 购物车视图
购物车视图 CartView 展示了购物车中的商品,并提供了删除商品的功能。
/// 购物车视图
struct CartView: View {
@Binding var cart: [Product]
@State private var isEditing = false
var body: some View {
List {
ForEach(cart) { product in
HStack {
Image(systemName: product.imageName)
.resizable()
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.cornerRadius(10)
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(product.name)
.font(.headline)
Text("\(product.price, specifier: "%.2f") 元")
.font(.subheadline)
}
}
}
.onDelete(perform: removeProducts)
}
.navigationTitle("购物车")
.navigationBarItems(trailing: Button(action: {
isEditing.toggle()
}) {
Text(isEditing ? "完成" : "编辑")
.foregroundColor(.blue)
.font(.headline)
})
.environment(\.editMode, isEditing ? .constant(.active) : .constant(.inactive))
}
private func removeProducts(at offsets: IndexSet) {
cart.remove(atOffsets: offsets)
}
}
#Preview {
NavigationView {
CartView(cart: .constant([
Product(name: "商品1",
price: 10.0,
description: "这是商品1的描述",
imageName: "photo"),
Product(name: "商品2",
price: 20.0,
description: "这是商品2的描述",
imageName: "book")
]))
}
}
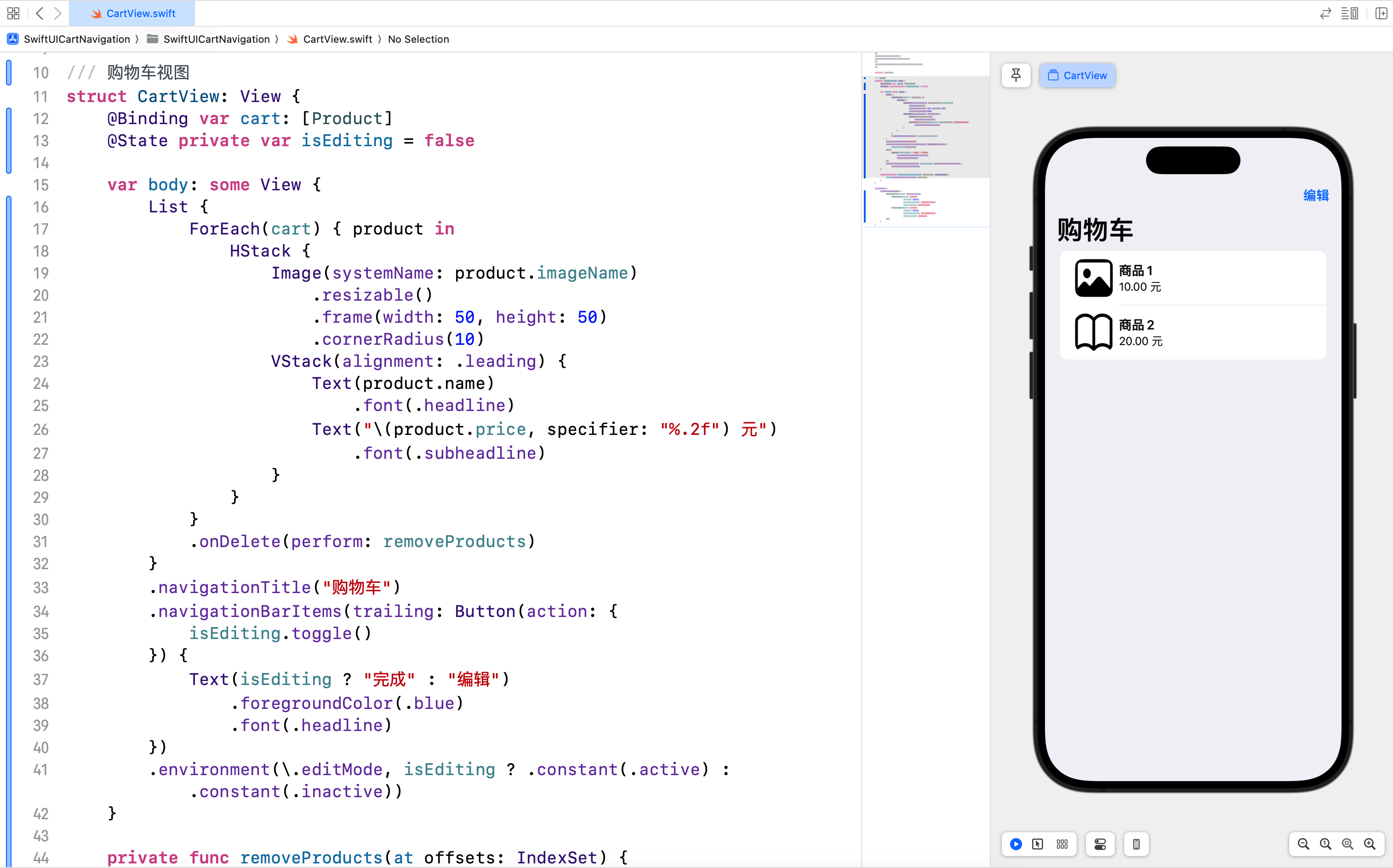
在这个视图中,我们展示了购物车中的商品,并提供了删除商品的功能。用户可以通过点击 EditButton 进入编辑模式,然后删除不需要的商品。
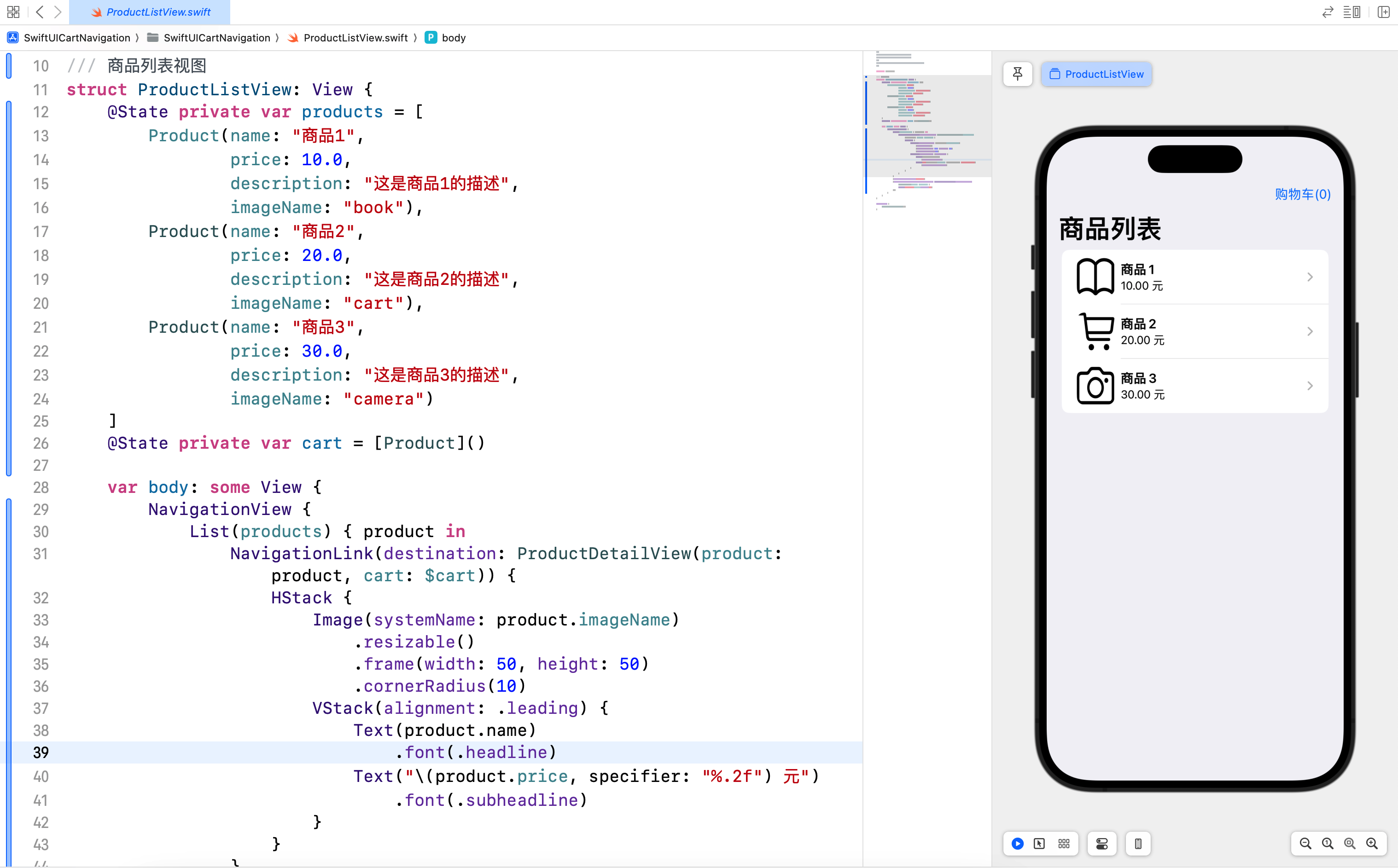
3.5 商品列表视图
在 ProductListView 中,我们展示了一个商品列表,每个商品项包括名称、价格和图像,并通过 NavigationLink 实现导航到商品详情页面。
/// 商品列表视图
struct ProductListView: View {
@State private var products = [
Product(name: "商品1",
price: 10.0,
description: "这是商品1的描述",
imageName: "book"),
Product(name: "商品2",
price: 20.0,
description: "这是商品2的描述",
imageName: "cart"),
Product(name: "商品3",
price: 30.0,
description: "这是商品3的描述",
imageName: "camera")
]
@State private var cart = [Product]()
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
List(products) { product in
NavigationLink(destination: ProductDetailView(product: product, cart: $cart)) {
HStack {
Image(systemName: product.imageName)
.resizable()
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
.cornerRadius(10)
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(product.name)
.font(.headline)
Text("\(product.price, specifier: "%.2f") 元")
.font(.subheadline)
}
}
}
}
.navigationTitle("商品列表")
.navigationBarItems(trailing: NavigationLink(destination: CartView(cart: $cart)) {
Text("购物车(\(cart.count))")
})
}
}
}
#Preview {
ProductListView()
}
3.6 案例总结
在这个购物车案例中,我们应用了以下技术点和注意事项:
- 数据模型:使用
Product结构体定义商品数据模型,包含商品的基本信息。 - 自定义列表单元格:通过
HStack和VStack组合视图元素,展示商品信息,包括名称、价格和图像。 - 导航:使用
NavigationLink实现视图之间的导航,包括商品列表到商品详情、商品列表到购物车的导航。 - 数据传递:通过
@Binding属性将购物车数据传递给子视图,实现商品添加到购物车的功能。 - 编辑模式:使用自定义的按钮实现购物车视图的编辑模式,用户可以删除购物车中的商品。
4. 结语
在本篇文章中,我们深入探讨了 SwiftUI 中的列表和导航,并通过一个综合的购物车案例将所学知识应用到实践中。通过学习如何创建和自定义列表,如何在列表中实现导航,以及如何在不同视图之间传递数据,您将能够构建出更加功能强大和用户友好的应用程序。下一篇文章将进一步探讨 SwiftUI 的 TabBar 与多页面应用,敬请期待。
- 本专栏文档及配套代码的 GitHub 地址:壹刀流的技术人生。
- 本文档配套项目名称:
SwiftUICartNavigation。